Java的日志框架很多,JUL, Log4J, Lobback, JCL, SLF4J等,之前也都大概知道它们是干什么的,网上也有各种讲怎么去配置的。但总觉得不得要领,这周结合官网文档和网上一些文章,把JUL, Log4J, JCL, SLF4J的源码过了一遍,爽。
JUL
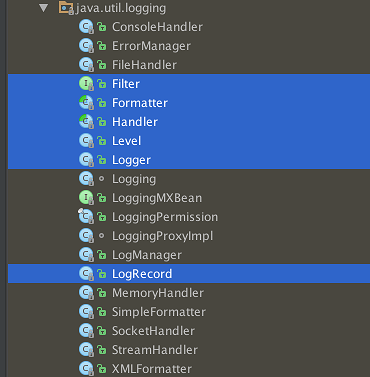
JUL相对来说比较简单,就这么几个类。Level定义了日志级别,这里的日志级别和其他框架的命名不太一样。
- SEVERE (highest value)
- WARNING
- INFO
- CONFIG
- FINE
- FINER
- FINEST (lowest value)
In addition there is a level OFF that can be used to turn off logging, and a level ALL that can be used to enable logging of all messages.
日志信息是保存在LogRecord中的,Logger首先判断日志级别,决定是否打印,然后调用Filter看是否过滤,最后调用Handler的publish方法来打印日志。Handler有多种,包括MemeoryHandler, ConsoleHandler,FileHandler等。在publish中,会获取Formatter来格式化日志,然后打印。中间稍微复杂的地方是有个日志层级的概念。这篇文章分析得很清楚,Java Logging: Logger Hierarchy,整个系列教程也很不错。
Log4j
2.X比1.X的代码无论是排版上还是注释上都好很多。
顺便了解了一下NDC和MDC
JCL
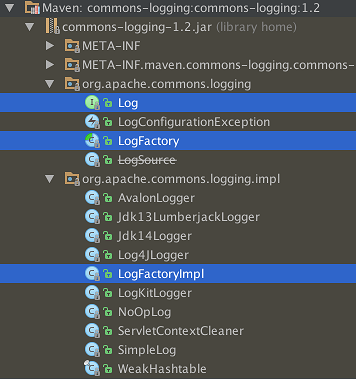
commons-logging只是做了一层包装,提供了一个门面接口,下层可以通过配置自由的选择各种日志框架,加载顺序如下
- Use a factory configuration attribute named
org.apache.commons.logging.Logto identify the requested implementation class. - Use the
org.apache.commons.logging.Logsystem property to identify the requested implementation class. - If Log4J is available, return an instance of
org.apache.commons.logging.impl.Log4JLogger. - If JDK 1.4 or later is available, return an instance of
org.apache.commons.logging.impl.Jdk14Logger. - Otherwise, return an instance of
org.apache.commons.logging.impl.SimpleLog.
SLF4J
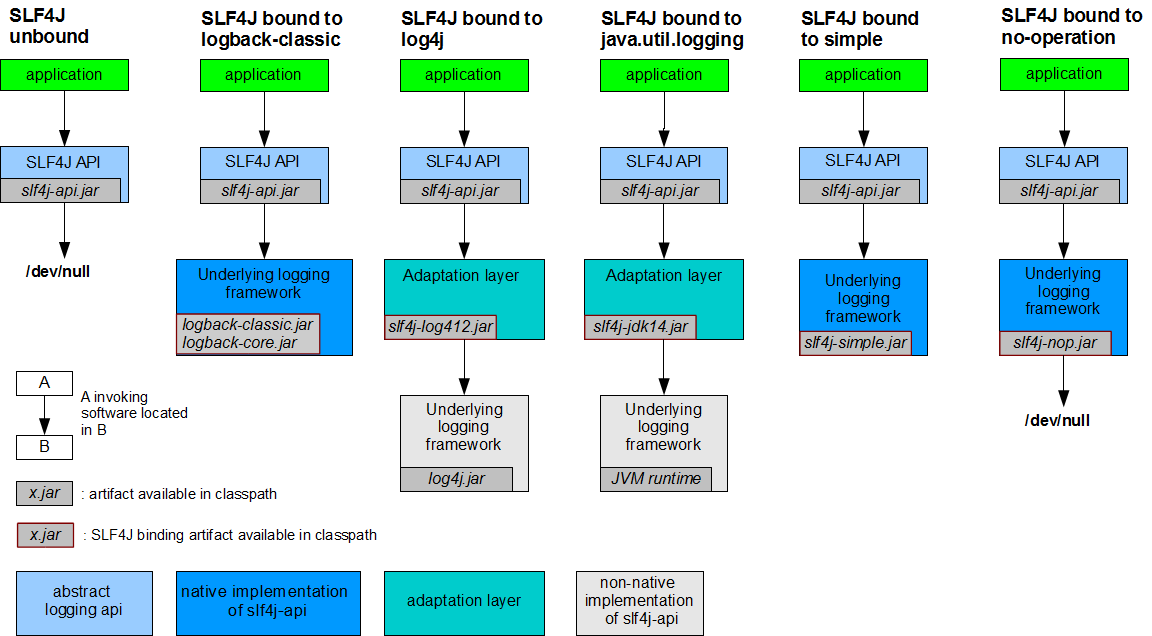
其他
关于这么多框架如何搭配使用,这篇文章总结的不错,slf4j、jcl、jul、log4j1、log4j2、logback大总结
为什么要使用SLF4J而不是Log4J中重点介绍了SLF4J中的占位符,以及它是如何提高效率的。
这是在Log4j中使用的方案1
2
3if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Processing trade with id: " + id + " symbol: " + symbol);
}
SLF4J的方案:1
logger.debug("Processing trade with id: {} and symbol : {} ", id, symbol);
明显后一种更优雅,且效率更高。